UWB (Ultra Wide Band) is the PHY defined in IEEE 802.15.4. There are two modes defined, High Rate Pulse (HRP) and Low Rate Pulse (LRP) and now we are more focused on HRP, which is widely used in a variety of applications with low date rate wireless connectivity and precision ranging.
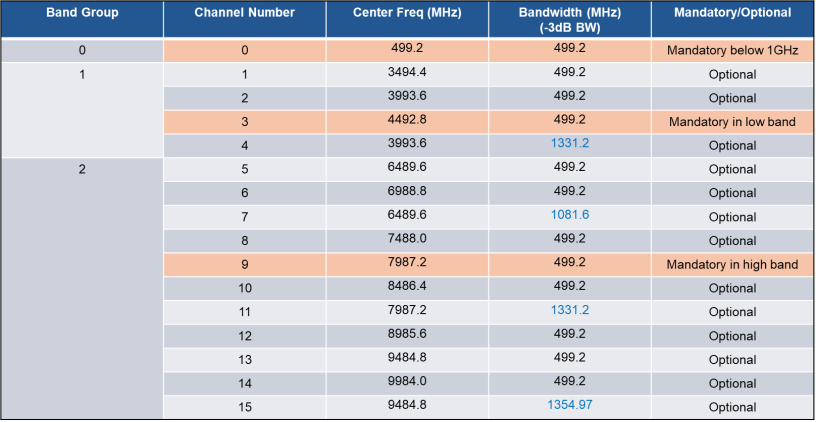
UWB devices operate in license-free frequency band. The frequency and channel assignments are defined in the figure below.
Figure 1. UWB Channel Assignment

For HRP UWB, A combination of burst position modulation (BPM) and binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) is used to modulate the symbols, with each symbol being composed of an active burst of UWB pulses. The
various data rates are supported through the use of variable-length bursts.
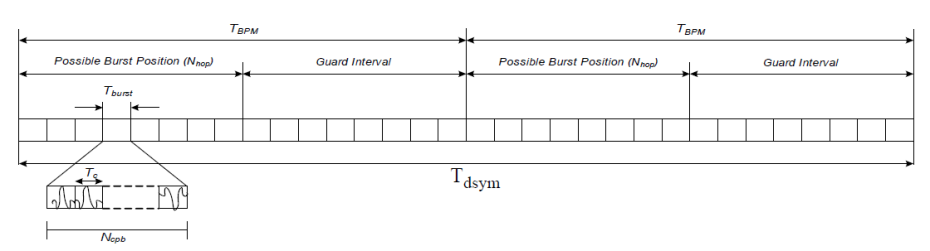
The symbol structure of HRP UWB is as Figure 1. The overall symbol period denoted by Tdsym is
divided into two BPM intervals. In the BPM-BPSK modulation scheme, each symbol is capable of carrying two bits of information: one bit is used to determine the position of a burst of pulses (first or second BPM interval), while an additional bit is used to modulate the phase (polarity) of this same burst. Guard interval is included to limit the amount of inter-symbol interference caused by multipath.
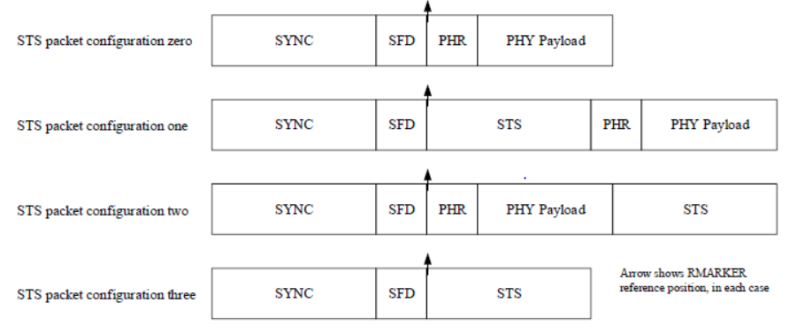
The physical frame is composed of three parts:
SHR (SYNC field): further split into two parts, the Preamble and SFD (start of frame delimiter) with variable lengths
PHR (PHY header): contains information about the data to be received, including the length of the data and the data rate used to transmit the data
Data (data field): actual payload (encoded user data)
Figure 2. Symbol Structure of HRP UWB
The 802.15.4z task group was established in response to the demand for enhanced operation. IEEE 802.15.4z enhances the UWB PHYs with additional coding and preamble options, improvements to existing modulations to increase the integrity and accuracy of the ranging measurements, and additional information element definitions to facilitate ranging information exchange. It also enhances the MAC to support control of time of flight ranging procedures and exchange ranging related information between the participating ranging devices.
In 802.15.4z, the HRP UWB PHY also includes optional modes to give reduced on-air time for higher density / lower power operation, and where the frame includes a ciphered sequence, denoted as the scrambled timestamp sequence (STS), to increase the integrity and accuracy of ranging measurements. A device incorporating these modes is referred to as an HRP-ERDEV.
An HRP-ERDEV shall support the following mandatory functionality:
Operation at the nominal 64 MHz PRF is referred to as the base pulse repetition frequency (BPRF) mode. By omitting the STS, the BPRF mode packet format reduces to a legacy packet format.
Operation at a higher PRF than the BPRF mode, referred to as the higher pulse repetition frequency (HPRF) mode.
The frame structure of HRP-ERDEV is shown in Figure 2, with STS in different positions. The STS consists of sequences of a pseudo-randomized pulses generated from AES-128. It will only be correctly received (correctly correlated in the receiver) when both TX and RX parties know the keys. It is secure against both accidental interference and intentional malicious attack.
Figure 3. Frame Structure of HRP-ERDEV